When we are concerned about impaired gas exchange nursing diagnosis, we must know that impaired gas exchange is the problem in the exchange of respiratory gases in the lungs.
The respiratory gases are oxygen and carbon dioxide. Impaired gas exchange is a significant health issue and it is important to move towards impaired gas exchange nursing diagnosis to know the reasons and treat it accordingly. Some of the sign and symptoms associated with impaired gas exchange include problems in breathing mechanisms and insufficient clearance of the airway.
What Are the Primary Symptoms Of Impaired Gas Exchange?
Before moving towards the impaired gas exchange nursing diagnosis, it is essential to know the symptoms of impaired gas exchange. Therefore, some of them are given below:
- Dyspnea: It is the shortness of breath.
- Change in breathing rate of the person.
- Cyanosis: It is the bluishness of skin due to a deficiency of oxygen level in the blood. It mainly occurs in nails and lips.
- Uneasiness
- Diaphoresis: It is the increased sweat production due to oxygen imbalance in the blood.
- Headache
- Vision problem
- Prickliness
- Tachycardia: Increase heart rate
- Reduction in oxygen level in blood
- Change in blood pH
What Are the Primary Reasons For Impaired Gas Exchange?
Impaired gas exchange is responsible for disruption in the exchange of respiratory gases. It is mainly due to airways shortening, blood, and breathing problems. However, a detailed description of the causes of impaired gas exchange is given below.
Also Read: What are the Nursing Implications? |
Blockage of airways in lungs:
- The impaired gas exchange may occur due to blockage of the alveoli or airways of the lungs.
- The airway may be blocked due to the entry of foreign particles into the airways.
Decrease in blood flow:
- Reduction of blood flow is also a significant problem of impaired gas exchange.
- A reduction in blood flow could be because of pulmonary embolism
- Reduction in blood flow to the heart results in cardiac failure.
- Any disease which is responsible for blood flow reduction can cause impaired gas exchange disease.
Read More: What Is Wet Nursing?
Breathing problems:
- COPD (Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease) is also responsible for impaired gas exchange. It is a disease that results in breathing problems.
- Some drugs can cause impaired gas exchange problems and these are known as opiates. These drugs lower the breathing rate of the patient in depth.
What Are The Goals And Achievements Of Impaired Gas Exchange Nursing Diagnosis?
There are many goals of impaired gas exchange nursing diagnosis. Some of them are given below:
Absence of respiratory problem:
- The main goal of impaired gas exchange nursing diagnosis is the reduction or nonappearance of respiratory problems.
- After recovery patient should not feel any respiratory problems.
- Read more: ADPIE nursing process- The 5 Stages of the ADPIE nursing process
Clearance of lung’s airways:
- Another goal of impaired gas exchange is to clear airways of the lungs.
- This thing also makes the patient free from respiratory problems.
Oxygen problem:
- To make the patient free from oxygen problems and other problems is another one.
- Furthermore, the patient should be free from the need of any inhaler or medication.
Also Read: What Are the Prerequisites for Nursing?
Proper oxygen consumption:
- As we know that there is a problem of oxygen exchange during impaired gas exchange. Therefore, the vital goal of impaired gas exchange nursing diagnosis is to regain average oxygen consumption.
Achievement of everyday life aspects:
After proper medication of impaired gas exchange, we can see following achievements:
- Patients can maintain typical gas exchange.
- They can attain the normal respiration rate of a resting person, which is about 12-20 per minute.
- The pulse oximeter reading will fall in normal range.
- Their blood gas level and heart rate will become normal.
What Tests Are Required For Impaired Gas Exchange Nursing Diagnosis?
For impaired gas exchange nursing diagnosis, you can simply check the respiratory function of the patient by observing his physical condition.
Here we will discuss the assessments and expected results of impaired gas exchange nursing diagnosis.
Also Read: Ineffective Coping Nursing Diagnosis | 2023
Respiratory test:
In the first test, you must evaluate these things:
- Rate of breathing.
- Depth of breathing.
- The struggle of a patient during breathing.
- Condition of respiratory muscle during breathing.
- The breathing pattern of the patient.
- The wideness of nostrils during breathing (Nasal flaring).
Results:
If you feel a slow or rapid breathing pattern, the patient may suffer from an impaired gas exchange (Gosselink & Stam, 2005). Slow breathing is termed hypoventilation.
Also Read: How Does Travel Nursing Work | 2023
Low oxygen level or hypoxia is also responsible for impaired gas exchange. It can be assessed by nasal flaring, and increased breathing rates.
Lung’s test:
Lung test is the second one for impaired gas exchange nursing diagnosis. In this you must assess:
- The surface area of the lungs.
- Lung’s Sound: It is termed as auscultation. If a person has no sound of breathing, then he may suffer from poor ventilation rate.
Results:
A patient may suffer from impaired gas exchange if he faces altered pattern of breathing. If a nurse hears a wheezing sound during breathing, it means the patient may suffer from alveoli blockage or hypoxia. And if the nurse did not hear a sound during breathing, then the patient may suffer from poor ventilation.
Body test:
In the third assessment test, you must note the following:
- The general behavior of the patient.
- Brain condition on restlessness.
- The ability of the patient to perform any tasks.
Results:
In 2015, Pascoal studied that “your patient may suffer from impaired gas exchange if you feel altered behavior and adverse mental condition”. He concluded that restlessness might occur if the patient has a change in breathing rate. And severe hypoxia may arise if there are cognitive changes.
Also Read: What Is A Nursing Philosophy? |2023 Guide
Pulmonary test:
In this test, you must check the following:
- Condition of lungs cells. Pulmonary infarction is of core importance.
- Breath sound condition
- Cough
- Pyrexia or fever
- Lung consolidation: Condition occurs when small airways of the lungs are changed with anything else.
- Lung’s pain
- Hemoptysis: It is the presence of blood in spitting and coughing.
- Fluid accumulation in layers of the lungs which is termed as pleural effusion
Results:
Hypoxia may occur if you feel bronchoconstriction in the area of infarction. An increase in dead space is also responsible for hypoxia which is the fundamental cause of impaired gas exchange.
Cardio test:
In this test, you must measure the following:
- Blood pressure
- Heart rate
Results:
Hypoxia and hypercapnia (increase in CO2 level) can cause an increase in heart rate and blood pressure.
Dysrhythmias or the absence of a heartbeat may also occur.
Oral test:
In this test, you need to know about the following:
- Color of the tongue.
- Condition of mucous membranes.
- Condition of nails.
Result:
Severe hypoxia occurs due to central cyanosis of the tongue and mucous membranes condition (Pahal et al., 2021). It might be severe if peripheral cyanosis occurs in the upper and lower extremities.
Respiratory gases test:
In this test, you must know the following:
- The CO2 level in the bloodstream.
Results:
Hypercapnia is of core importance in impaired gas exchange nursing diagnosis. It is the increase in carbon dioxide levels in the blood. If a patient is suffering from hypercapnia, he will have these symptoms:
- Headache
- Lethargy
- Inability to understand things
- Unconsciousness
Oxygen test:
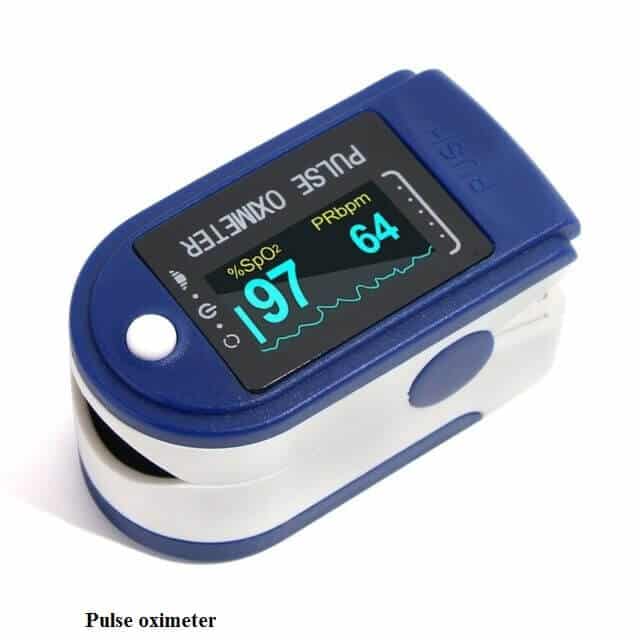
In this test, you should measure the following:
- Oxygen saturation
An Instrument for Oxygen Saturation:
You can measure oxygen saturation with the help of a pulse oximeter. A pulse oximeter is one of the best tools to measure the oxygen changes in the blood.
Also Read: What Does Prn Mean in Nursing? | 2023 Guide
Results:
The average oxygen concentration in blood is about 95% to 100%. If a person has an oxygen concentration less than 80%, they may suffer from an oxygen problem.
ABG test:
In this test, you must know the following:
- The partial pressure of gases in the blood.
Results:
Hypoxemia and respiratory acidosis occur as PaCO2 increases and PaO2 decreases. In severe conditions, the PaCO2 will increase to a dangerous level, and the respiration rate will also decrease.
Some patients with COPD face a decline in respiratory reserves. Respiratory failure may also occur.
Read More: Step-by-Step Guide Cleaning an Injection Site
Internal function test:
In this test, you must measure the following:
- How oxygenation is affected by position change.
- Arterial blood gas tests (ABGs)
- SvO2, that is the measure of oxygen content returned to the right side of the heart.
- Pulse oximetry: It is the measure of oxygen saturation by an oximeter.
Results:
Putting the lungs in a most conceded area in a dependent position will increase the ventilation rate. In the dependent position, the rate of perfusion is maximum.
Nutrition test:
In this test, you must know the following:
- Nutritional status of the person.
- Obesity
Results:
It is the second most big assessment of impaired gas exchange nursing diagnosis. Now we will discuss some nutritional issues and their effects.
Obesity:

It causes
- Restriction in the movement of the diaphragm.
- Increase in risk of the lung collapsing or
- Respiratory infections.
- Decrease in ventilation.
- Strenuous breathing also known as difficult breathing.
Malnutrition:
It can cause:
- Reduction in respiration.
- Reduction in muscle strength.
Also Read: What Is Pre-Nursing? | 2023 Guide
Blood test:
In this test, you should check the following:
- Level of hemoglobin (Hgb test).
Results:
A person with a low hemoglobin level will face low oxygen pickup by alveolar capillaries.
The patient will also face low oxygen delivery to tissues.
MRI test:
In this test, you must know the following:
- Chest X-ray report.
Result:
The Chest X-ray studies of the patient will disclose the factor for impaired gas exchange.
Cough test:
In this test, you must know the following things:
- Condition of the patient during cough out secretions.
- Color of the sputum.
- Quantity of saliva.
- Consistency of sputum.
Results:
The presence of secretions in sputum will indicate poor gas exchange.
Water test:
- In this test, you must know about the water intake of the patient.
Results:
A hydration test is essential for impaired gas exchange nursing diagnosis.
Overhydration can cause heart failure, and dehydration may cause an inability to secretion clearance. It is seen in COPD patients and pneumonia patients.
Read More: Top 10 Best Stethoscope For Nurses Review & Buying Guide
Some Interventions That Are Used During Impaired Gas Exchange Nursing Diagnosis
Here we will discuss nursing interventions for impaired gas exchange
1. Home adjustment:
In this test, you must note the following:
- Pollutants or irritating agents cause impaired gas exchange.
Results:
Irritants are mainly responsible for impaired gas exchange problems. A pollutant can cause disturbance in oxygen uptake of the lungs and thus can cause impaired gas exchange.
To prevent this, you must change the patient’s environment according to a need. For example, the use of an air filter can reduce dust.
2. Head adjustment:
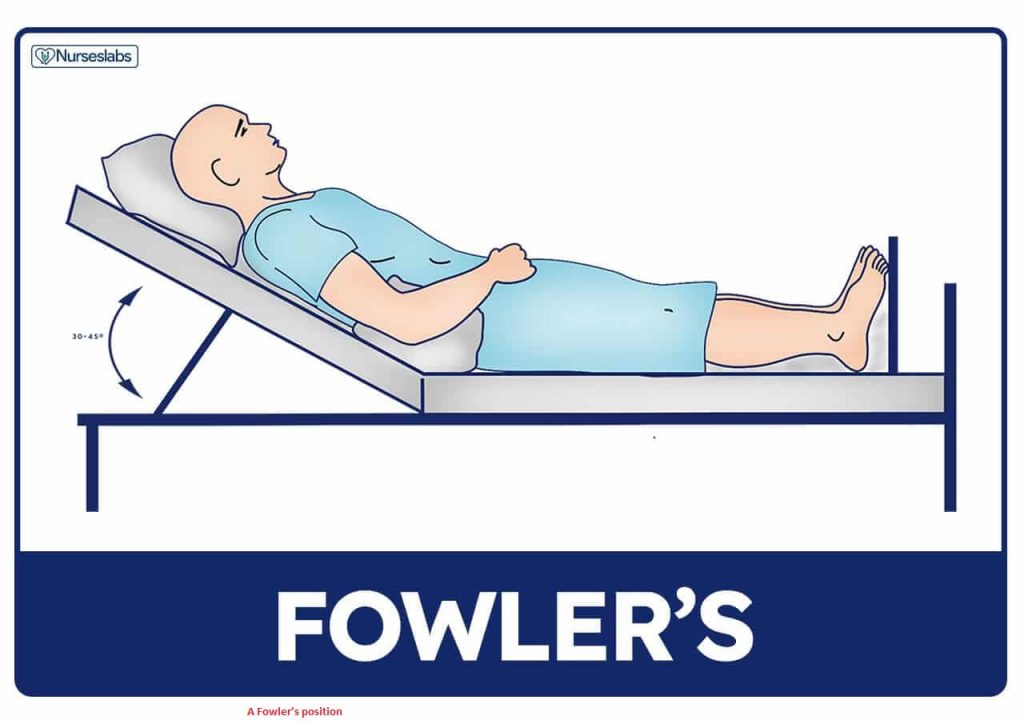
In this adjustment, you must do the following things:
- The patient’s head must be elevated in bed.
- When the patient is in a supine position, the head of the bed must be at 45 degrees. In other words, the patient should be in fowler’s position.
Results:
A Fowler’s position is responsible for the following:
- increases in thoracic capacity.
- Lung expansion that prevents abdominal content from flocking.
- Descent of diaphragm.
3. Position checking:
In this involvement, you must ensure that patient does not fall into the bed.
Reasons:
A falling or slumped position may compress the diaphragm of the patient. It will also decrease lung expansion which, as a result, causes impaired gas exchange.
4. Ventilation increase:
The nurse must assist the patient in increasing ventilation. You can increase the ventilation rate by changing position if a patient has unilateral lung disease.
Reasons:
Gravity and hydrostatic pressure on the lungs can improve the rate of breathing. The excellent side must be down when the patient is in a side position.
Atelectasis or pulmonary embolus should be upward. If a lung is affected by a lung hemorrhage or an abscess, then you must place the affected lung downward.
It will reduce the delivery of disease to a healthy lung.
5. Ambulation:
A nurse should assist in improving the ambulation (Ability to walk without any assistance) of the patient.
Importance of ambulation:
It will help to
Improve lung expansion.
Improve lung secretion clearance.
Promote deep breathing.
6. Trendelenburg position:

If a patient has ascites (Accumulation of fluid in space within your abdomen) or suffering from obesity, you should use the Trendelenburg position. It is also 45 degrees.
Importance of Trendelenburg position:
It will decrease breathing rates and increase tidal volumes.
Oxygen saturation:
As a nurse, you should maintain oxygen saturation as per the instructions of the physician.
You can use supplements to adjust the value of supplemental oxygen. Normal oxygen saturation is about 90 percent. It is an important step in impaired gas exchange nursing diagnosis.
8. Oxygen concentration during activity:
If a patient is allowed to eat, as a nurse you should adjust the oxygen concentration accordingly and differently. You should change oxygen delivery during eating because more oxygen is consumed.
And you must return the oxygen delivery to normal after the meal.
9. Suction:
If a patient is unable to clear the airways of the lungs, you should make suction. It will clear the secretions. If the patient’s airways get blocked, he may suffer from impaired gas exchange.
10. Reduce anxiety:
As a nurse, you should assist the patient in remaining free from anxiety and ask him to be comfortable.
Effect of anxiety:
It will cause
- Dyspnea
- Increase in breathing rate.
Read More: IV Therapy Tips & Tricks: How to Hit a Vein Every Time
Impaired Gas Exchange Nursing Diagnosis- Conclusion:
In impaired gas exchange nursing diagnosis, you can perform different tests. You can diagnose the patient by respiration test, cardio test, oral test, and so many others. You should assist the patient with suction, oxygen saturation, position changing, etc.
Impaired gas exchange nursing diagnosis- FAQs:
How to diagnose impaired gas exchange?
You can check impaired gas exchange by:
- Rate of breathing.
- Depth of breathing.
- The struggle of a patient during breathing.
- The surface area of the lungs.
- Lung consolidation
- Lung’s pain
- Hemoptysis
- Blood pressure
- Heart rate
- Oxygen saturation
- You can measure oxygen saturation with the help of a pulse oximeter. A pulse oximeter is one of the best tools to measure the oxygen changes in the blood.
What is the reason for impaired gas exchange?
- The impaired gas exchange may occur due to blockage of the alveoli or airways of the lungs.
- Reduction of blood flow is also a significant problem of impaired gas exchange.
- COPD is also responsible for impaired gas exchange. It is a disease that results in breathing problems
- Some drugs can cause impaired gas exchange problems. Drugs that cause impaired gas exchange are opiates. These drugs lower the breathing rate of the patient in depth.
What are the symptoms of impaired gas exchange?
- Dyspnea: It is the shortness of breath.
- Change in breathing rate of the person.
- Cyanosis
- Diaphoresis: It is the increased sweat production due to oxygen imbalance in the blood.
- Headache
- Vision problem
For more info visit: Nursing Guides
References and Sources
Recommended sources, interesting articles, and references about Ineffective Airway Clearance to further your reading.
- Doenges, Marilynn E., et al. Nursing Diagnosis Manual: Planning, Individualizing, and Documenting Client Care. F.A. Davis, 2005.
- Gulanick, Meg, and Judith L. Myers. Nursing Care Plans: Diagnoses, Interventions, and Outcomes. Elsevier/Mosby, 2014.
- Herdman, T. Heather, and Shigemi Kamitsuru. Nursing Diagnoses: Definitions and Classification 2018-2020. Thieme, 2018.
- Pascoal, L. M., Lopes, M. V. D. O., Chaves, D. B. R., Beltrão, B. A., Silva, V. M. D., & Monteiro, F. P. M. (2015). Impaired gas exchange: accuracy of defining characteristics in children with acute respiratory infection1. Revista latino-americana de enfermagem, 23, 491-499.
- Pahal, P., & Goyal, A. (2021). Central and Peripheral Cyanosis. StatPearls [Internet].
- Ackley, B., & Ladwig, G. (2014). Nursing diagnosis handbook (10th ed). Maryland Heights: Mosby Elsevier.
- Gulanick, M., & Myers, J. (2014). Nursing care plans (8th ed.). Elsevier.
- Ignatavicius, D., & Workman, M. (2016). Medical-surgical nursing (8th ed.). Elsevier.
- Yoost, B. L., & Crawford, L. R. (2019). Fundamentals of Nursing E-Book: Active Learning for Collaborative Practice. Elsevier Health Sciences.
